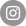
Typical or average insulin in units per meal and in total for the day
0
1
0
The amount of insulin needed per meal or day varies greatly depending on a person’s metabolic health, insulin sensitivity, body weight, activity levels, and specific dietary composition. Here’s an overview of typical or average insulin needs for individuals on different diets:

1. Standard American Diet (SAD)
Carbohydrate content: High (45–65% of total calories).
Blood sugar impact: High due to frequent consumption of refined carbs and sugars.
Insulin usage:
• Per meal: 4–10+ units of insulin, depending on carb intake (e.g., 50–100+ grams per meal).
• Daily total: ~40–60+ units for someone with normal insulin sensitivity; individuals with insulin resistance may require more (60–100+ units).
2. High-Fat, Low-Carb Diet (HFLC)
Carbohydrate content: Moderate-to-low (20–100 grams per day).
Blood sugar impact: Lower compared to SAD, as fewer carbs are consumed.
Insulin usage:
• Per meal: 1–4 units of insulin, depending on carb intake (e.g., ~10–30 grams per meal).
• Daily total: ~20–30 units for those with moderate insulin sensitivity.
3. Ketogenic Diet (Very Low-Carb, High-Fat)
Carbohydrate content: Very low (typically <20–50 grams per day).
Blood sugar impact: Minimal, as carbs are replaced by fats and protein.
Insulin usage:
• Per meal: ~0–1 unit of insulin (most meals may not require exogenous insulin if carbs are extremely low).
• Daily total: ~5–15 units, depending on protein intake and individual sensitivity.
Key Considerations:
1. Protein’s Role: Protein can stimulate a mild insulin response even in low-carb diets. This is factored into dosing for ketogenic and HFLC diets.
2. Endogenous vs. Exogenous Insulin: Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes or advanced Type 2 Diabetes rely on exogenous insulin, while others may see reduced endogenous insulin secretion on low-carb or ketogenic diets.
3. Activity Level: Physical activity significantly reduces insulin requirements for all diets.
4. Individual Variability: Insulin needs vary by insulin resistance, body weight, and genetic factors.
%20(320%20x%20.png)